graphql-engine
Remote schemas
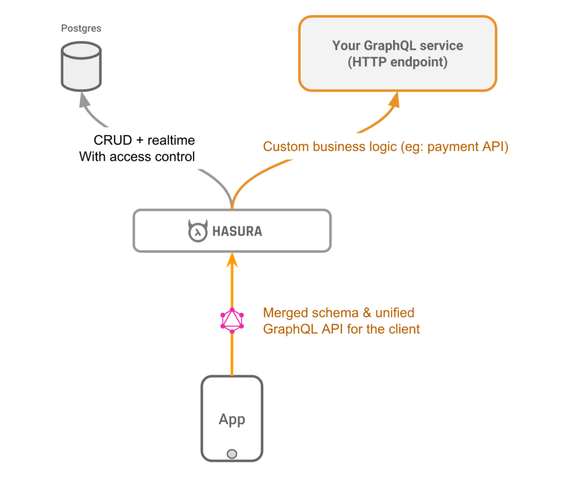
Hasura gives you CRUD + realtime GraphQL APIs with authorization & access control. However, in many cases, you will need to write APIs (queries, mutations) that contain custom logic. For example, implementing a payment API, or querying data that is not in your database.
Hasura has the ability to merge remote GraphQL schemas and provide a unified GraphQL API. Think of it like automated schema merging. All you need to do is build your own GraphQL service and then provide the HTTP endpoint to Hasura. Your GraphQL service can be written in any language or framework.
Remote schemas are ideal for use cases such as:
- Customizing mutations (e.g. running validations before inserts)
- Supporting features like payments, etc. and providing a consistent interface to access them i.e. behind the GraphQL Engine’s API
- Fetching disparate data from other sources (e.g. from a weather API or another database)
To support custom business logic, you’ll need to create a custom GraphQL server (see boilerplates) and merge its schema with GraphQL Engine’s.
Demo (40 seconds)
Merge remote GraphQL schemas (YouTube link)
Quickstart
The fastest way to try remote schema out is via Heroku.
-
Click on the following button to deploy GraphQL Engine on Heroku with the free Postgres add-on:
-
Open the Hasura console
Visit
https://<app-name>.herokuapp.com(replace <app-name> with your app name) to open the admin console. -
Merge your first remote schema and query it
In the admin console, open the
Remote Schemastab and click on theAddbutton. Fill in the following details:- Remote Schema name:
countries(an alias for this remote schema). - GraphQL server URL:
https://countries.trevorblades.com/(a public GraphQL API that we’ll use to quickly check out this feature; maintained by @trevorblades. - Ignore the remaining configuration settings and click on the
Add Remote Schemabutton.
Head to the ``GraphiQL` tab and run the following query (paste it in the query window on the left and click the ▶️ (play) button):
{ countries { emoji name languages { name native } } }You can explore the GraphQL types from the remote schema using the
Docsexplorer in the top right corner of theGraphiQLinterface. - Remote Schema name:
Boilerplates
Boilerplates for custom GraphQL servers in popular languages/frameworks are available.
- Regular boilerplates that can be deployed anywhere.
- Serverless boilerplates that can be deployed on serverless platforms like AWS Lambda, etc.
Please note that boilerplates for more languages, frameworks, serverless platforms, etc. are being iterated upon and community contributions are very welcome.
Caveats
Current limitations:
- Nomenclature: Type names and node names need to be unique across all merged schemas (case-sensitive match). In the next few iterations, support for merging types with the same name and structure will be available.
- Nodes from different GraphQL servers cannot be used in the same query/mutation. All top-level nodes have to be from the same GraphQL server.
- Subscriptions on remote GraphQL server are not supported.
These limitations will be addressed in upcoming versions.
Documentation
Read the complete documentation.
Translations
This document is available in the following translations: